In a world increasingly attuned to sustainability and eco-conscious choices, the term “Organic Cotton” has become synonymous with ethical and environmentally friendly textiles. This versatile and eco-friendly fabric is reshaping the way we think about clothing, bedding, and more.
Organic Cotton is more than just a fabric. It represents a movement towards a more sustainable and ethical fashion industry. Unlike conventional cotton, which is grown using harmful pesticides and synthetic fertilizers, organic cotton is cultivated using natural farming methods. This means that the cotton is grown without the use of any toxic chemicals, promoting healthier soil, water, and air quality.
Moreover, chemical-free cotton farmers prioritize the well-being of workers and communities. By adhering to fair trade practices and ensuring a safe working environment, chemical-free cotton supports the livelihoods of farmers and promotes social justice in the supply chain.
Join us as we embark on a journey through the world of Organic Cotton. Explore its benefits, discover the stories behind the fabric, and learn how you can make a difference by choosing eco-friendly cotton products. Together, we can create a more sustainable and ethical world, one thread at a time.
- Organic Cotton: a Fabric of Quality
- The Farming Practices of ECO-Friendly Cotton
- Organic Cotton VS Conventional Cotton
- The Ecological Footprint of Organic Cotton Cultivation
- Navigating Sustainability in Organic Cotton Farming: Landfill and Pest Management
- The Benefits and Drawbacks of Organic Cotton
- Choosing The Right Fabric
- FAQs: Your Questions Answered
Organic Cotton: a Fabric of Quality
As consumers become more conscious of their impact on the environment, the demand for organic cotton continues to grow. Major fashion brands are embracing this movement, incorporating natural cotton into their collections and gradually shifting towards a more sustainable future.
When it comes to quality of the fabric, organic cotton holds its ground. The absence of harsh chemicals allows for the preservation of the cotton’s natural softness, strength, and breathability. Clothing made from organic cotton feels luxurious against the skin and provides a comfortable, hypoallergenic alternative to synthetic fabrics.

The Farming Practices of ECO-Friendly Cotton
The roots of organic cotton trace back to the early 20th century when forward-thinking farmers embarked on pioneering journeys into pesticide-free and sustainable cotton farming practices. These individuals recognized the harmful effects that synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers had on the environment, as well as on their own health.
Driven by a desire to protect the land and their communities, these farmers began experimenting with alternative farming methods that relied on natural processes and inputs. They sought to work in harmony with nature, rather than against it. By embracing practices such as crop rotation, composting, and biological pest control, they aimed to create a more balanced and sustainable agricultural system.
While these early efforts were significant, it wasn’t until the late 20th century that the modern organic cotton movement truly gained momentum. This resurgence was ignited by growing concerns regarding the environmental and health impacts associated with conventional cotton farming.
Organic Cotton VS Conventional Cotton
Conventional cotton production is heavily reliant on synthetic pesticides and herbicides, which can have devastating effects on the surrounding ecosystem. These chemicals can contaminate water sources, harm beneficial insects and animals, and contribute to soil degradation. Moreover, the exposure to these toxic substances has been linked to various health issues for farmers and communities living near cotton fields.
In contrast, eco-friendly cotton farming takes a holistic approach to agriculture. It emphasizes soil health, biodiversity, and the use of natural and sustainable farming practices. Organic farmers rely on techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and integrated pest management to promote natural pest control and enhance the fertility of the soil.
Organic cotton is also grown using non-GMO seeds, which helps preserve the integrity of the crop and promotes biodiversity in the agricultural landscape. By avoiding the use of synthetic chemicals, eco-friendly cotton farming provides a safer and healthier working environment for farmers and their communities.
Furthermore, organic cotton production includes rigorous certification processes and standards to ensure the integrity and transparency of the supply chain. This allows consumers to make informed choices and support sustainable and ethically produced textiles.
As the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products continues to grow, organic cotton has gained recognition as a viable alternative to conventional cotton. It offers the opportunity to support responsible farming practices, protect the environment, and promote social justice in the textile industry.
By choosing organic cotton, we can contribute to a more sustainable future, where fashion and textiles are produced in harmony with nature and our well-being.
Production Countries
Organic cotton, with its promise of eco-friendliness and ethical production, finds its cultivation footprint spread across a multitude of countries. The leading global producers of organic cotton include India, Turkey, Kyrgyzstan, China, and the United States. Each of these nations plays a crucial role in the global effort toward sustainable and responsible cotton farming.
India, known for its long-standing tradition of cotton cultivation, has emerged as the largest producer of organic cotton in recent years. With the country’s rich agricultural heritage and favorable climate conditions, Indian farmers have been able to adopt organic farming methods effectively. This has not only benefited the environment but also improved the livelihoods of rural farming communities.
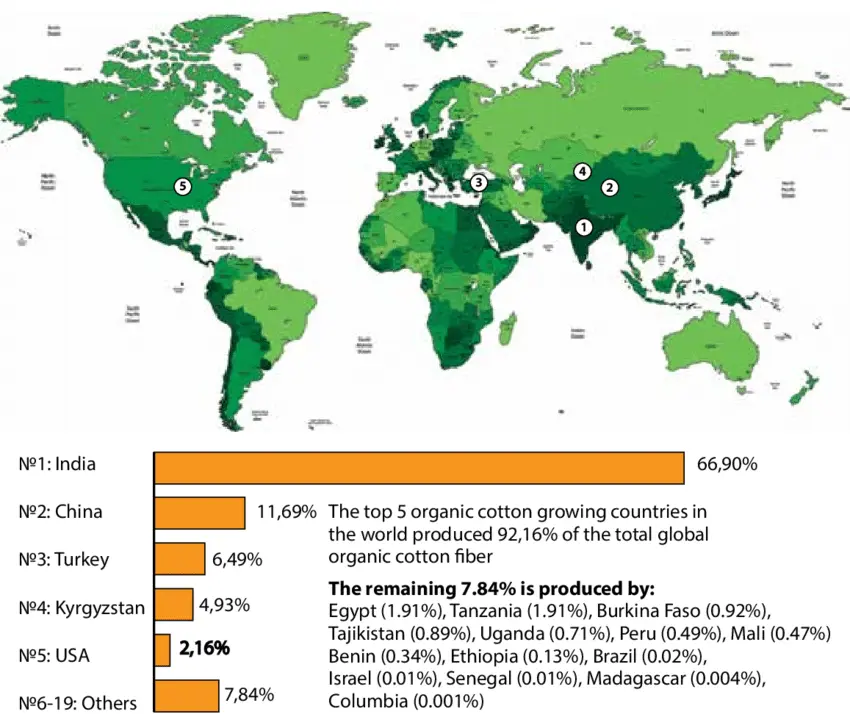
In China, the organic cotton industry has gained momentum in recent years. The government’s support for organic farming and the adoption of strict certification standards have encouraged more farmers to transition from conventional to organic practices. This has not only reduced the environmental impact of cotton cultivation but has also provided consumers worldwide with a wider range of sustainable textile options.
Turkey, another significant player in organic cotton production, stands out for its dedication to sustainable farming practices. Turkish farmers have taken proactive steps to reduce chemical inputs and implement organic techniques to preserve soil health and biodiversity. The outcome has been the production of high-quality eco-friendly cotton, sought after by global textile manufacturers.
Kyrgyzstan ranks fourth in global organic cotton production, contributing approximately 4.93% of the world’s supply. Its success highlights the growing recognition of sustainable agriculture and the positive impact of organic farming practices on both the economy and the environment. Kyrgyzstan’s commitment to organic cotton expands our understanding of the global impact of sustainable textile practices.
The United States, has also embraced organic cotton farming. American farmers, driven by consumer demand for organic products, have been transitioning their fields to organic practices. This shift has proven beneficial in preserving soil fertility, reducing water usage, and minimizing the use of harmful pesticides. As a result, the United States remains a key contributor to the global organic cotton market.
Collectively, these countries lead the way in demonstrating that organic cotton production is not just a trend but a viable solution for a more sustainable and responsible textile industry. The growth of eco-friendly cotton cultivation in these regions serves as an inspiration and motivator for other nations to follow suit. By supporting and promoting organic cotton, we can contribute to a greener future and a more ethical fashion industry.
The Ecological Footprint of Organic Cotton Cultivation
The ecological footprint of organic cotton cultivation is relatively lower compared to conventional cotton farming, primarily due to several environmentally friendly practices associated with organic farming methods. Here are key aspects of the ecological footprint of natural cotton cultivation:
Reduced Water Usage: Organic cotton typically relies on rain-fed agriculture or more efficient irrigation systems, resulting in lower water consumption compared to conventional cotton. Conventional cotton is notorious for its water-intensive nature, and organic cotton’s reduced water footprint addresses this issue.
Lower Energy Consumption: Organic cotton farming tends to have a lower carbon footprint because it doesn’t depend heavily on energy-intensive synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. By avoiding the production and application of these chemicals, natural cotton reduces the energy input required for farming.
Pesticide-Free Cultivation: Organic cotton is grown without synthetic pesticides. This reduces the risk of pesticide runoff into nearby water bodies, minimizing contamination and ecological harm to aquatic ecosystems. It also helps protect non-target organisms such as beneficial insects.
Healthier Soil: Organic cotton farming emphasizes soil health through practices like crop rotation and the use of organic matter, such as compost. Healthier soil ecosystems enhance biodiversity and improve carbon sequestration, contributing to a more sustainable environment.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Organic cotton farming can contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions due to reduced fertilizer use. Synthetic fertilizers in conventional cotton farming release nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas. Organic practices help mitigate this effect.
Biodiversity Conservation: Organic cotton farms often support greater biodiversity by avoiding monoculture planting. Diverse ecosystems on organic farms can include beneficial insects, birds, and native plants, which contribute to a healthier environment.
Soil Erosion Prevention: Organic farming methods help prevent soil erosion by maintaining soil structure and promoting root growth. This protects against land degradation, which can have long-lasting ecological consequences.
Overall, the ecological footprint of organic cotton cultivation reflects its commitment to more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. By addressing key environmental challenges associated with conventional cotton farming, chemical-free cotton contributes to a greener and more eco-conscious textile industry.
Navigating Sustainability in Organic Cotton Farming: Landfill and Pest Management
Addressing landfill concerns and managing pests organically are imperative components of sustainable organic cotton farming. By prioritizing these aspects, farmers can contribute to a more environmentally friendly and socially responsible approach to cotton production.
Landfill Concerns
One of the significant challenges faced by the textile industry is the massive amount of waste generated throughout the manufacturing process. Conventional cotton farming often utilizes synthetic pesticides and fertilizers that contaminate the soil and waterways. Additionally, the production of synthetic materials and the disposal of unused fabric contribute to the accumulation of non-biodegradable waste in landfills.
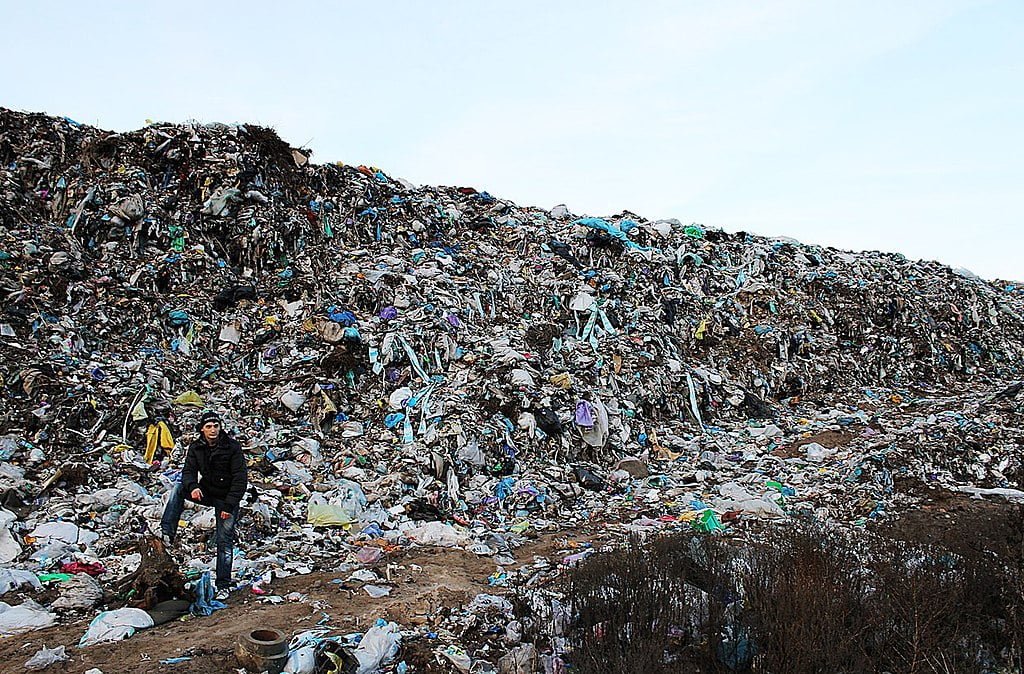

Sustainable organic cotton farming seeks to minimize landfill concerns by implementing eco-friendly practices at various stages. Farmers use natural and biodegradable alternatives to synthetic chemicals, such as organic fertilizers and biological pest control methods. These approaches not only reduce the environmental impact but also promote healthier soils and ecosystems.
Furthermore, organic cotton farmers emphasize the efficient use of resources to minimize waste. This includes proper irrigation techniques, crop rotation, and soil conservation practices. By conserving water and nutrients, farmers can enhance the long-term productivity of the land while minimizing the need for excessive inputs.
Pest Control
In the realm of pest management, organic cotton farming prioritizes sustainable and environmentally friendly methods. This involves the use of beneficial insects, natural predators, and traps to control pests instead of relying solely on chemical pesticides. By maintaining a balanced ecosystem, farmers can naturally suppress pest populations and minimize the harm caused to beneficial insects.
Organic cotton farming relies on natural and sustainable methods to control pests, as it avoids synthetic pesticides. By taking a holistic approach to pest management, farmers can effectively minimize the impact on the environment and reduce the reliance on synthetic pesticides. Here are some common organic pest management strategies:
Crop Rotation: Farmers frequently rotate cotton crops with other plants to disrupt pest life cycles and reduce pest pressure naturally.
Biological Pest Control: Beneficial insects and organisms, like ladybugs, lacewings, and nematodes, are introduced to the fields to prey on or parasitize cotton pests.

Trap Crops: Some crops are planted nearby to attract pests away from the cotton crop, serving as “trap crops” that can be managed more easily.
Companion Planting: Planting companion crops that deter pests or attract beneficial insects can help reduce pest damage.
Organic Sprays: Organic-approved sprays made from neem oil, garlic, or hot pepper solutions can be used as natural pest deterrents.
Hand Picking: In some cases, hand picking or vacuuming pests off the cotton plants is employed to control infestations.
Beneficial Plants: Certain plants, such as marigolds, can be interplanted with cotton to repel pests.
Overall, organic cotton farming aims to minimize the environmental impact associated with synthetic pesticides and promote more natural and sustainable approaches to pest management, which is in line with the broader goals of organic and sustainable agriculture.
Organic cotton farming often requires careful monitoring and adaptation to local conditions. Crop yields may vary, and successful pest management may require a combination of these techniques. While organic pest management can be effective, it may not completely eliminate pest damage, and farmers may accept some level of crop loss as part of sustainable practices.
In conclusion, addressing landfill concerns and managing pests organically are vital components of sustainable organic cotton farming. By adopting eco-friendly practices and implementing integrated pest management techniques, farmers can promote a more sustainable and socially responsible approach to cotton production. Together, these efforts contribute to the preservation of our natural resources and the well-being of both the environment and the communities involved in the textile industry.

The Benefits and Drawbacks of Organic Cotton
The benefits of eco-friendly cotton extend beyond clothing. The use of organic cotton in bedding and home textiles ensures that you are surrounding yourself with a safe and natural environment as you sleep or relax. From sheets to towels, choosing non-GMO cotton means that every aspect of your daily life can be touched by its soothing touch.
While organic cotton is often hailed as a sustainable option, it is important to critically examine its purported advantages and disadvantages. Many question the true impact of organic cotton, and its claims of being environmentally friendly. In this section, we delve into the realities and raise skepticism regarding the practicality and efficacy of this seemingly eco-conscious textile choice. Our goal is to offer a clear and comprehensive perspective to aid in informed decision-making when it comes to this eco-conscious textile choice.
Related: THE CERTIFICATION FOR ECO-FRIENDLY FABRICS
Advantages
Organic cotton is not only a sustainable choice, but it also brings several advantages when compared to conventional cotton. Here are some key benefits of using organic cotton:
- Environmental Friendliness: Organic cotton is a sustainable choice that promotes environmental well-being. Unlike conventionally grown cotton, organic cotton is produced without the use of toxic chemicals, such as pesticides or synthetic fertilizers, herbicides, or genetically modified seeds. By relying on natural farming methods, organic cotton reduces the exposure of farmers and workers to harmful chemicals and protects the biodiversity of surrounding ecosystems. Additionally, organic farming practices prioritize soil health, water conservation, and ecosystem preservation, contributing to a healthier planet for future generations.
- Healthier for Farmers: Conventional cotton farming involves the use of hazardous chemicals that can be harmful to farmers’ health. Organic cotton farming ensures a safer working environment for cotton farmers, reducing their exposure to harmful toxins. This promotes the overall well-being of farming communities.
- Biodegradable: One of the advantages of organic cotton is its biodegradability. Unlike synthetic fabrics, which can take hundreds of years to break down in landfills, organic cotton decomposes relatively quickly. This biodegradability minimizes the environmental impact of discarded organic cotton products, ensuring they won’t contribute to the ever-growing waste problem. By choosing organic cotton, you’re making a responsible choice that aligns with the principles of circular economy and reduces your ecological footprint.
- Allergy and Irritation-free: Organic cotton is naturally hypoallergenic and free from chemical residues. This makes it a great choice for people with sensitive skin or allergies. The soft and breathable nature of organic cotton promotes comfort and reduces the risk of skin irritation.
- Quality and Durability: Organic cotton products are known for their superior quality and durability. The fibers are carefully cultivated, resulting in softer and stronger materials. This means that your organic cotton garments and home textiles are likely to last longer and hold up well to regular use and washing.
- Comfort: When it comes to clothing, comfort is paramount. Organic cotton fabric offers the perfect balance of softness, breathability, and durability. The absence of toxic chemicals in the growing and processing of organic cotton ensures that the resulting fabric is gentle on the skin and doesn’t cause irritation or discomfort. Whether you’re wearing organic cotton t-shirts, dresses, or bedding, you can enjoy the luxurious feel and cozy comfort that comes from choosing natural, organic fibers.
- Hypoallergenic: For people with sensitive skin or allergies, organic cotton can be a game-changer. The lack of synthetic chemicals, pesticides, and dyes in organic cotton reduces the risk of skin irritations, allergies, and respiratory problems that can be triggered by conventional cotton. By opting for hypoallergenic organic cotton products, you can prioritize your well-being and enjoy the softness and comfort of fabrics that are kind to both you and the environment.
- Supporting Fair Trade: Many organic cotton brands prioritize fair trade practices, ensuring that farmers and workers are paid fairly and work in safe conditions. By choosing organic cotton, you actively contribute to the empowerment and livelihood improvement of these individuals.
- Reduced Water Footprint: Organic cotton farming techniques focus on water conservation and minimizing water usage. Compared to conventional cotton, organic cotton requires less water for growth and irrigation. This helps in conserving this precious resource for other essential needs.
Opting for organic cotton supports sustainable farming practices, protects the environment, and promotes healthier living for both producers and consumers.
Disadvantages
It is important to consider the potential disadvantages associated with organic cotton production as well.
- Higher Cost: One of the main drawbacks of organic cotton is its higher cost compared to conventional cotton. This is primarily due to the additional labor, care, and resources required in the cultivation of natural cotton. Chemical-free cotton farming adheres to strict guidelines that prohibit the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified seeds. As a result, farmers have to rely on more labor-intensive practices such as crop rotation, hand weeding, and natural pest control methods. These extra efforts not only increase the production costs but also require continuous monitoring and management to ensure adherence to organic standards. Consequently, the added expenses are passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices for organic cotton products.
- Lower Yields: Another factor to consider is that organic cotton farms may experience lower yields compared to conventional cotton farms. This can be attributed to the absence of synthetic fertilizers that provide a concentrated nutrient boost to conventionally grown cotton. Non-GMO farming relies on the use of natural fertilizers, such as compost and animal manure, which often take time to break down and release nutrients. This slower nutrient release, coupled with the reliance on crop rotation for soil health, may result in reduced cotton yields. The lower productivity can impact the supply chain and ultimately influence the pricing of organic cotton products.
- Land Resources: Organic cotton farming requires larger land areas to achieve the same amount of production as conventional methods. This can put pressure on land resources and limit the availability of fertile agricultural land for other crops or purposes. It is crucial to carefully manage land use and ensure a balanced approach to agricultural practices.
- Transition Period: Transitioning a conventional cotton farm to organic practices can be a challenging and time-consuming process. Converting a farm into an organic operation involves adopting organic farming techniques, eliminating the use of synthetic inputs, and implementing sustainable practices. The transition period typically takes a few years, during which farmers need to follow organic farming standards without being able to label their products as certified organic. This transitional phase can be financially demanding for farmers as they invest in new farming methods and face potential yield reductions during the initial stages of the transition. It requires determination, patience, and financial stability to successfully make the switch to organic cotton farming.
- Limited Availability: While demand for organic cotton products is on the rise, they may still be less readily available compared to conventional cotton items. The logistics of sourcing and processing organic cotton can be more complex compared to conventional cotton. The limited availability of eco-friendly cotton, especially on a global scale, can pose challenges for manufacturers and brands seeking to incorporate it into their products. However, as consumer awareness and demand continue to grow, there has been an increasing effort to expand the production and availability of eco-friendly cotton products. Supply chain transparency and traceability become crucial in maintaining the integrity of organic cotton throughout the production process. Many sustainable fashion brands and retailers are now prioritizing organic and ethically sourced materials, making them more accessible to conscious consumers. Nevertheless, the wider adoption of organic cotton still requires time and further investments in sustainable farming practices.
- Water Management: Despite its sustainability credentials, organic cotton production still consumes a significant amount of water. Cotton is a highly water-intensive crop, and organic cotton is no exception. The irrigation requirements for natural cotton can strain local water sources, especially in regions already facing water scarcity issues. Proper water management strategies and technologies are essential to mitigate this challenge.
In conclusion, the higher cost, lower yields, transition period, and limited availability are important factors to consider when it comes to eco-friendly cotton products. While they may present challenges in terms of pricing and accessibility, many consumers prioritize the environmental benefits and sustainability that organic cotton offers. With continued commitment from farmers, brands, and consumers, the pesticide-free cotton industry has the potential to further flourish and make a positive impact on the textile industry as a whole.
Choosing The Right Fabric
When it comes to sustainable fabrics, organic cotton is certainly a popular choice. However, it’s worth exploring other eco-friendly options that can make a positive impact on our planet. In my informative blog post titled “The Truth About Eco-Friendly Fabrics“, I delve into the topic and highlight the top five sustainable fabrics to consider: organic cotton, hemp, bamboo, Tencel, and a hemp/organic cotton blend. Let’s bring the benefits of each of these fabrics to the table.
Organic cotton is a versatile and sustainable fabric that is gaining popularity in the textile industry for its numerous benefits. It is grown without the use of harmful pesticides and chemicals, making it better for the environment and our health. This natural fiber is soft, breathable, and hypoallergenic, making it ideal for people with sensitive skin.
Hemp, which is known for its strength and durability. Hemp fabric is highly breathable and has a natural resistance to UV rays, making it suitable for outdoor clothing and accessories. It also requires less water and land to grow, making it a more sustainable choice.
Bamboo fabric is another eco-friendly option that has gained popularity in recent years. Bamboo grows quickly and does not require the use of pesticides or fertilizers. The fabric derived from bamboo is soft, lightweight, and has natural moisture-wicking properties, keeping you cool and comfortable even in hot and humid climates.
Tencel: For those looking for a fabric that combines the best of both worlds, Tencel is an excellent choice. Made from sustainably sourced wood pulp, Tencel is known for its silky feel and exceptional moisture-wicking abilities. It is also biodegradable, making it an eco-friendly option.
Hemp/organic cotton blends: If you’re looking for a fabric that offers a balance between durability and comfort, hemp/organic cotton blends are worth considering. These blends combine the strength and durability of hemp with the softness and breathability of natural cotton. The result is a fabric that is not only comfortable to wear but also long-lasting and sustainable.
When it comes to choosing the right fabric, consider your specific needs and priorities. Organic cotton, hemp, bamboo, Tencel, and hemp/organic cotton blends all have their unique advantages and properties that can suit different applications and personal preferences. By opting for these sustainable fabrics, you can make a positive impact on the environment while enjoying high-quality and comfortable textiles.
FAQs: Your Questions Answered
What is organic cotton?
Organic cotton is a type of cotton produced using organic farming methods, which prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and synthetic fertilizers. It promotes more sustainable and environmentally friendly cotton production.
How is Non-GMO cotton different from conventional cotton?
Non-GMO, Organic cotton is grown without synthetic chemicals, while conventional cotton relies heavily on pesticides and synthetic fertilizers. Eco-friendly cotton farming also emphasizes soil health, biodiversity, and ethical labor practices.
Is organic cotton more expensive than conventional cotton?
Yes, organic cotton products often come with a higher price tag because organic farming methods require more labor-intensive practices and can yield slightly lower quantities compared to conventional cotton.
What certifications should I look for when buying organic cotton products?
Look for certifications like GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) and OEKO-TEX Standard 100. These certifications ensure that the textile products meet specific environmental and social criteria and are free from harmful substances. Learn about Certifications for Eco-Friendly Fabrics.
Does organic cotton use less water than conventional cotton?
Organic cotton farming often utilizes more sustainable water management practices, such as rain-fed agriculture and efficient irrigation systems, which can lead to lower water consumption compared to conventional cotton farming.
Can organic cotton clothing be as comfortable as conventional cotton clothing?
Yes, organic cotton clothing can be just as comfortable as conventional cotton clothing. Natural cotton retains the softness and breathability that make cotton a popular choice for textiles.
What are the benefits of choosing organic cotton for bedding?
Organic cotton bedding offers comfort, breathability, and the assurance of pesticide-free and eco-friendly production. It can promote a healthier and more sustainable sleep environment.
Are there any disadvantages to using organic cotton?
The main disadvantage is that organic cotton products can be more expensive due to the higher cost of production. Additionally, some eco-friendly cotton farms may have slightly lower yields compared to conventional farms.
Does organic cotton contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
Organic cotton farming can contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional cotton farming. Reduced synthetic fertilizer use and healthier soil management can help mitigate carbon emissions.



